URANOS
The Ultra Rapid Adaptable Neutron-Only Simulation for Environmental Research
M. Köhli1, M. Schrön2, S. Zacharias2, P. Dietrich2 and U. Schmidt1
1 Physikalisches Institut, Heidelberg University2 Department of Monitoring and Exploration Technologies, UFZ Leipzig

Contact:
M. Köhli, M. Schrön
Abstract
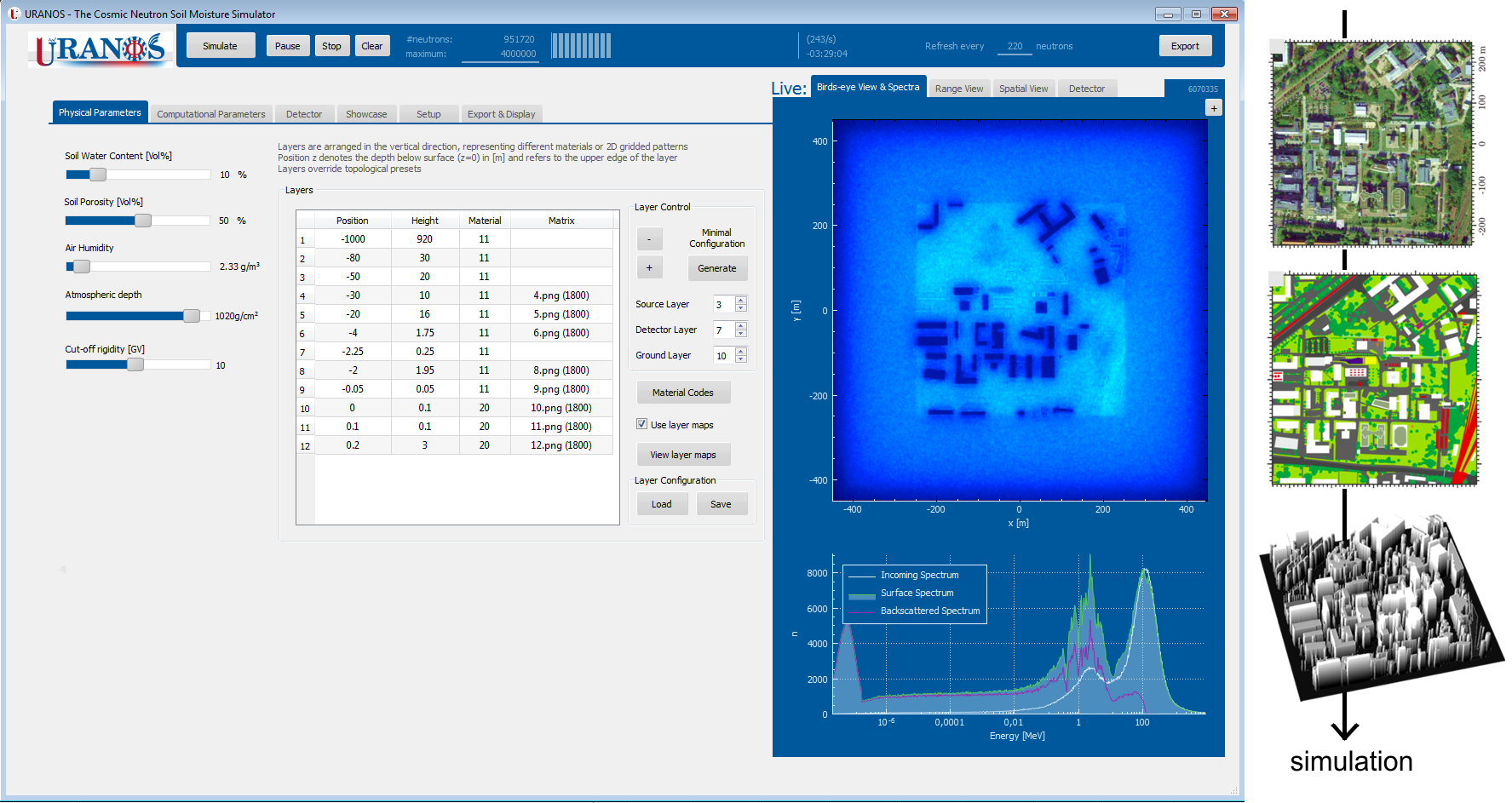
The Monte Carlo code URANOS was specifically tailored to address the open questions of cosmic-ray neutron sensing for environmental applications (Köhli et al. 2021). As the model has been developed further, it also proofed to be useful for neutron spin echo detectors in other research fields (Köhli et al. 2016). The model is able to predict the response of cosmic-ray neutrons to user-defined and spatially variable conditions in the soil, atmosphere, and biosphere. URANOS is very efficient, as it only accounts for the most relevant neutron interaction processes, namely elastic collisions, inelastic collisions, absorption, and evaporation.The main model features are:
- voxel engine,
- tracking of particle histories from creation to detection (ray-casting),
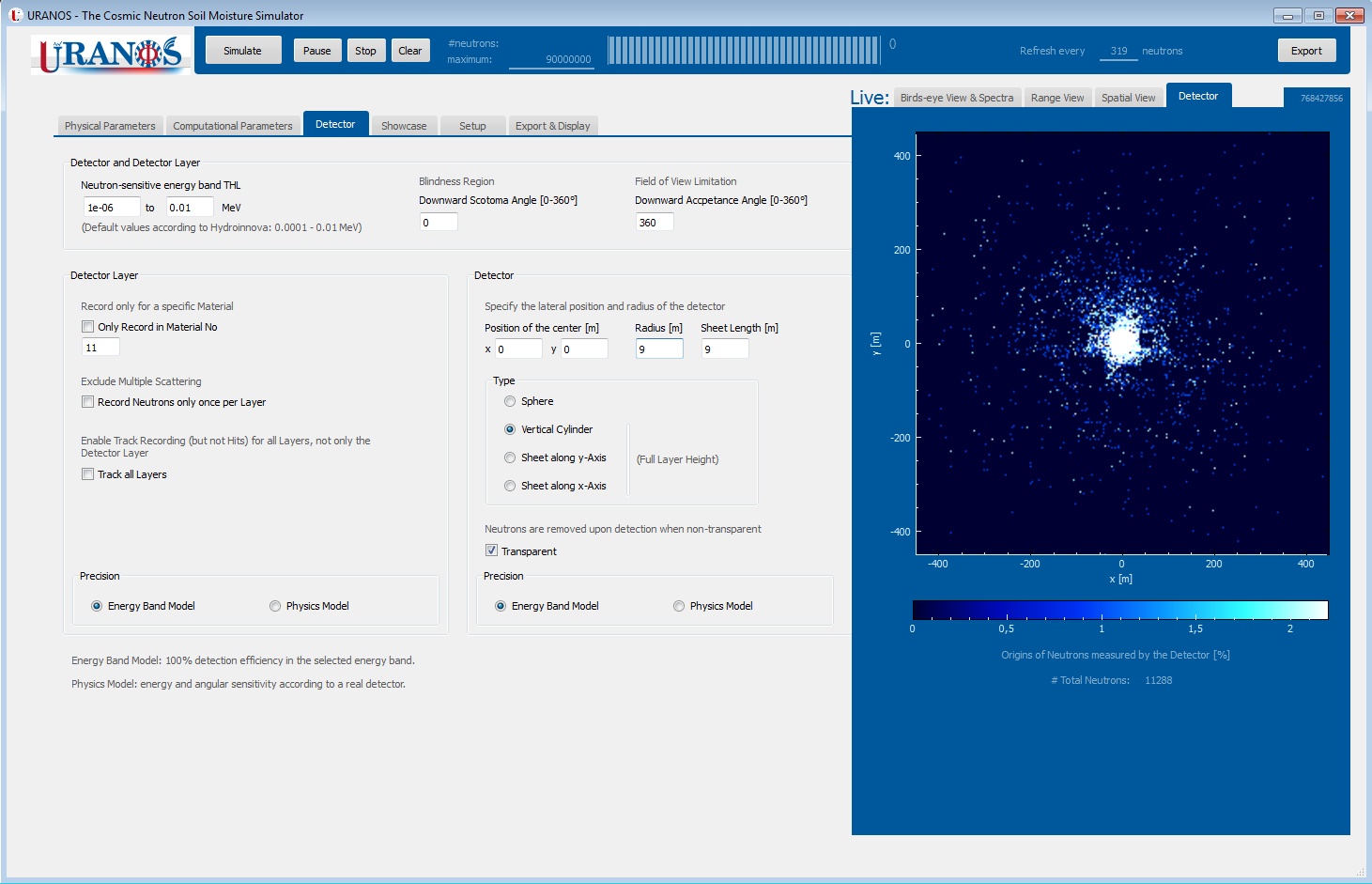
- detector representation as layers or cylinders,
- automatic model and material setup based on color codes in 2D bitmap images
Acknowledgements
URANOS was developed for the project "Neutron Detectors for the MIEZE method" funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), grant identifier: 05K10VHA. Source code and support for URANOS can be provided by M. Köhli. The research was funded and supported by Terrestrial Environmental Observatories (TERENO), which is a joint collaboration program involving several Helmholtz Research Centers in Germany.Resources
URANOS Main Program
- URANOS v1.30 (Windows 7-11, 64bit, ROOT 6.30.02)
- URANOS v1.16 (Windows 7-11, 32bit)
- URANOS v1.23 (Ubuntu 20, 64bit, QT 5.14.2)
- URANOS v1.28 (Ubuntu 22, 64bit, QT 5.15.3)
- URANOS v1.25 (Ubuntu 23.04, 64bit, QT 5.14.2)
- URANOS v1.28 (Ubuntu 24, 64bit, QT 5.15.3)
- URANOS v1.12 (CentOS 7, 64bit, QT 5.9.7)
- URANOS v1.19 (CentOS 7, 64bit, QT 5.13.1)
URANOS previous version
URANOS Additional Dependencies
- ROOT 6.30.02 (URANOS 64bit)
- ROOT 6.28.06 (URANOS 64bit)
- ROOT 6.22.08 (URANOS 32bit)
- Incoming Spectrum Definition
- Cross Section Files (v0.99+)
Suplementaries
Documentation
GitLab Repository
GitHub Repository
- URANOS GitHub (currently deprecated)
UFZ Leipzig Website
Additional information, publications and mailing lists:Cosmic-Sense Project
Support
For technical support, questions or adaptation of the source code for your own project, please contacturanos(_a)physi.uni-heidelberg.de
URANOS software model description
- Köhli, M., et al., 2023, "URANOS v1.0 - the Ultra Rapid Adaptable Neutron-Only Simulation for Environmental Research", Geosci. Model. Dev., 16, 449-477, doi:10.5194/gmd-16-449-2023
Reference publication list
- Rasche, D., et al., 2023, "A change in perspective: downhole cosmic-ray neutron sensing for the estimation of soil moisture", Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 27(16), 3059-3082, doi:10.5194/hess-27-3059-2023
- Brogi, C., et al., 2023, "Monitoring Irrigation in Small Orchards with Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensors", Sensors 2023, 23(5), 2378, doi:10.3390/s23052378
- Schrön, M., et al., 2023, "Signal contribution of distant areas to cosmic-ray neutron sensors - implications for footprint and sensitivity", Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 27(3), 723-738, doi:10.5194/gmd-16-449-2023
- Brogi, C., et al., 2022, "Feasibility of irrigation monitoring with cosmic-ray neutron sensors", Geosci. Instrum. Method. Data Syst., 11, 451-469, doi:10.5194/gi-11-451-2022<
- Köhli, M., et al., 2022, "Feasibility of UXO detection via pulsed neutron-neutron logging", Appl. Radiat. Isot., 110403, doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110403
- Francke, T., et al., 2022, "Assessing the feasibility of a directional cosmic-ray neutron sensing sensor for estimating soil moisture", Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst., 11(1), 75-92, doi:10.5194/gi-11-75-2022
- Rasche, D., et al., 2021, "Towards disentangling heterogeneous soil moisture patterns in cosmic-ray neutron sensor footprints", Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 25, 6547-6566, doi:10.5194/hess-25-6547-2021
- Köhli, M., et al., 2021, "Potential von Impulse-Neutron-Neutron-Logging zur Kampfmitteldetektion", Altlasten Spektrum, 6, 193-198, doi:10.37307/j.1864-8371.2021.06.03
- Köhli, M., et al., 2021, "Soil Moisture and Air Humidity dependence of the above-ground cosmic-ray neutron intensity", Frontiers in Water, 2, 1-15, doi:10.3389/frwa.2020.544847
- Badiee, A., et al., 2021, "Using Additional Moderator to Control the Footprint of a COSMOS Rover for Soil Moisture Measurement", Water Resources Research, 57, e2020WR028478, doi:10.1029/2020WR028478
- Weimar, J., et al., 2020, "Large-scale boron-lined neutron detection systems as a 3He alternative for Cosmic Ray Neutron Sensing", Frontiers in Water, 2, 1-16, doi:10.3389/frwa.2020.00016
- Schattan, P., et al., 2019, "Sensing area-average snow water equivalent with cosmic-ray neutrons: the influence of fractional snow cover", Water Resources Research, 55, 10796-10812, doi:10.1029/2019WR025647
- Li, D., et al., 2019, "Can Drip Irrigation be Scheduled with Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensing?", Vadose Zone J., 18:190053, doi:10.2136/vzj2019.05.0053
- Köhli, M., et al., 2018, "Response Functions for Detectors in Cosmic Ray Neutron Sensing", Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 902, 184-189, doi:10.1016/j.nima.2018.06.052
- Schrön, M., et al., 2018, "The Cosmic-Ray Neutron Rover - Mobile Surveys of Field Soil Moisture and the Influence of Roads", Water Resources Research, doi: 10.1029/2017WR021719
- Schrön, M., et al., 2018, "Intercomparison of cosmic-ray neutron sensors and water balance monitoring in an urban environment", Geoscientific Instrumentation, Methods and Data Systems, 7, 83-99, doi:10.5194/gi-7-83-2018
- Schrön, M., et al., 2017, "Improving calibration and validation of cosmic-ray neutron sensors in the light of spatial sensitivity", Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 21, 5009-5030, doi:10.5194/hess-21-5009-2017
- Köhli, M., et al., 2017, "Novel Neutron Detectors based on the Time Projection Method", Physica B: Condensed Matter - ICNS Proceedings, doi:10.1016/j.physb.2018.03.026
- Köhli, M., et al., 2016, "Efficiency and spatial resolution of the CASCADE thermal neutron detector", Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 828, 242-249, doi:10.1016/j.nima.2016.05.014
- Schrön, M., et al., 2015, "Monitoring Environmental Water with Ground Albedo Neutrons and Correction for Incoming Cosmic Rays with Neutron Monitor Data". In: 34th International Cosmic-Ray Conference (ICRC 2015). Proceedings of Science.
- Köhli, M., Schrön, M. et al., 2015, "Footprint characteristics revised for field-scale soil moisture monitoring with cosmic-ray neutrons", Water Resources Research, 51, 5772-5790, doi:10.1002/2015WR017169
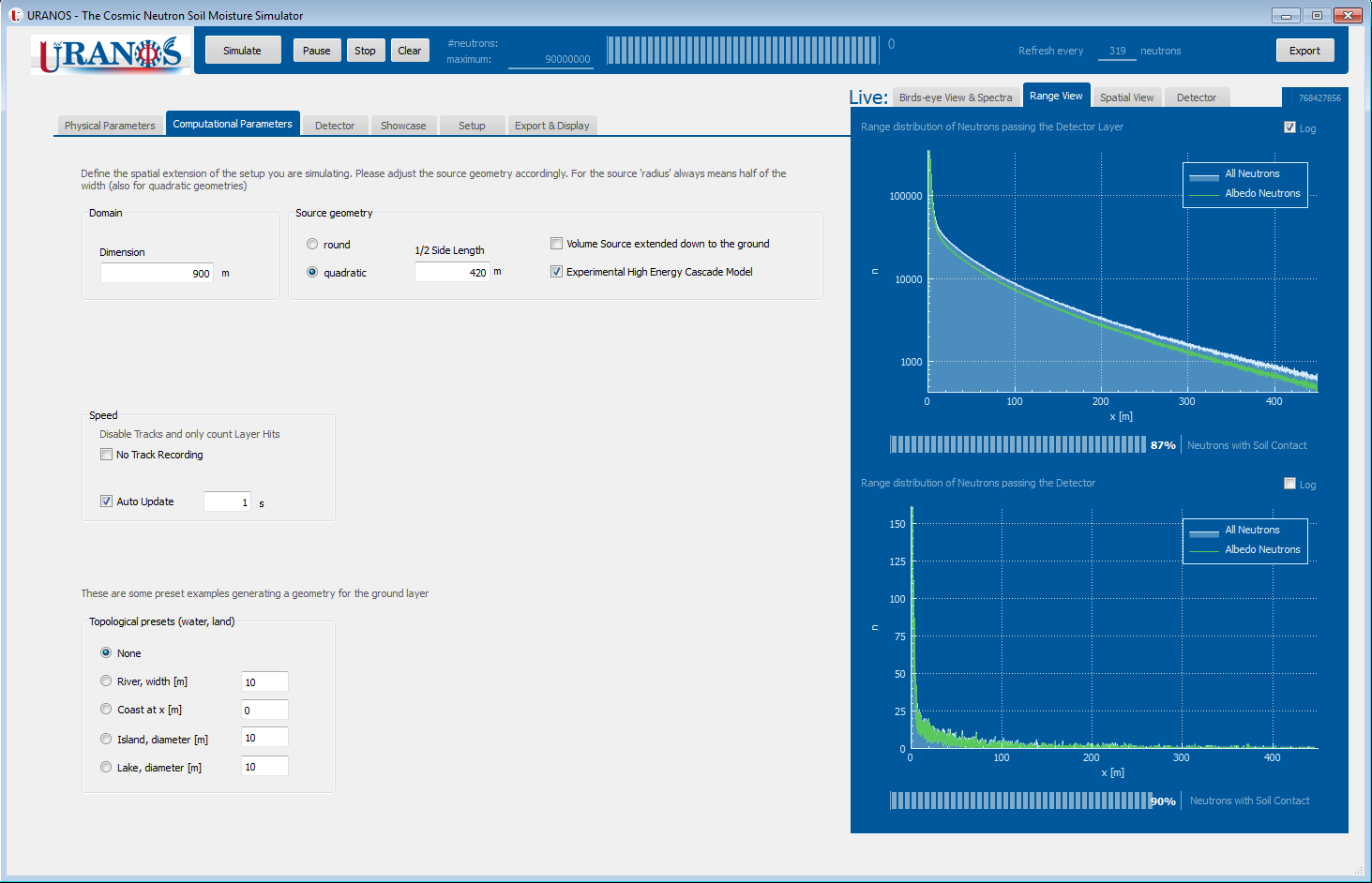
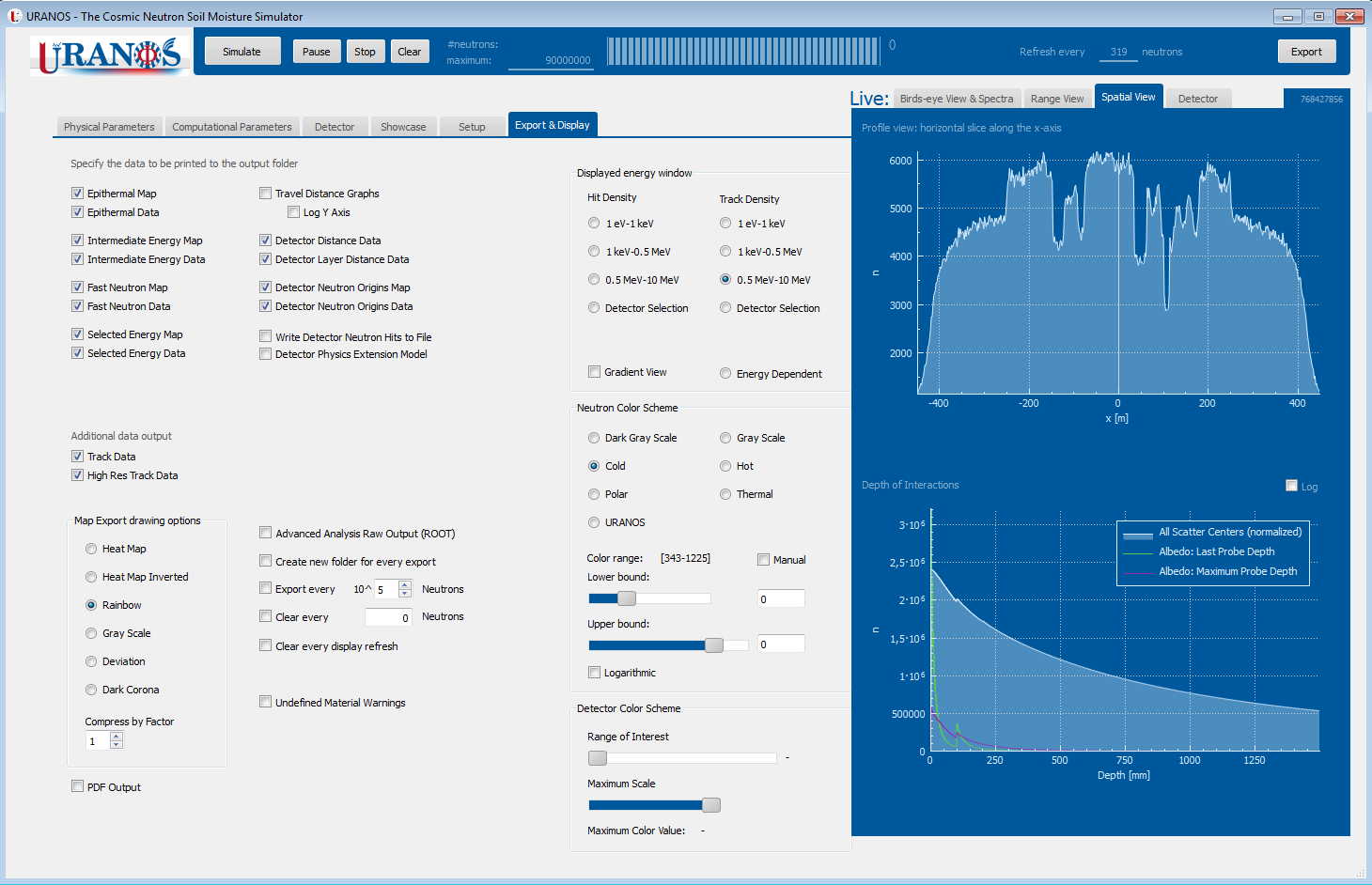
Screenshots